Computer Vision in Remote Sensing
Land-use and land-cover change detection
Computer vision and remote sensing technologies are significant in detecting land-use and land-cover changes around the world due to their ability to process large amounts of data from various sources, including satellite imagery, aerial photographs, and LiDAR data.
 |
|---|
| Lake Tana Basin raster data imagery collected by Landsat Satellites |
Remote sensing technologies can provide accurate and reliable information on land-use and land-cover changes, which can be used for various applications, such as urban planning, natural resource management, and biodiversity conservation.
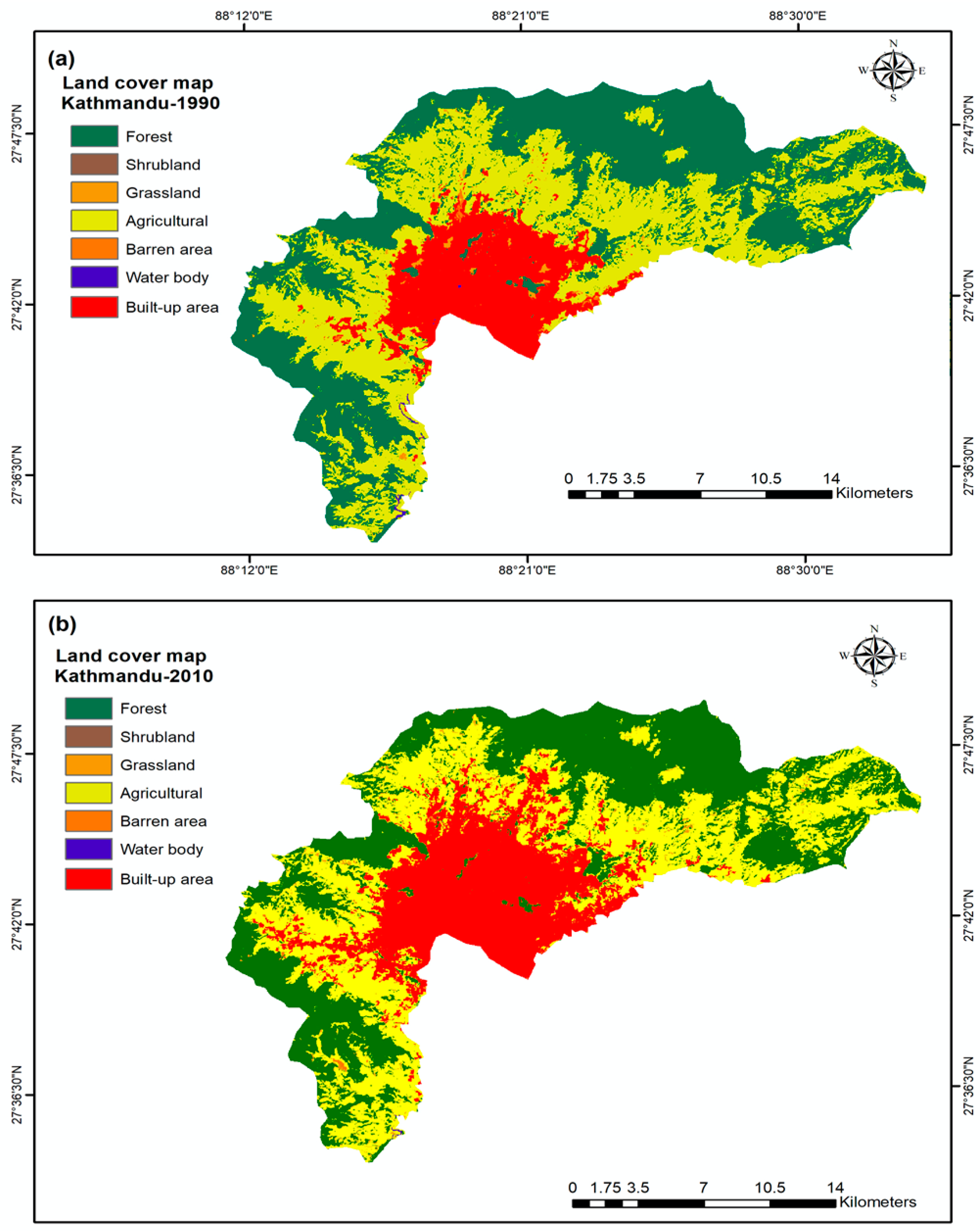 |
|---|
| Land use and land cover change (LULC) change map of the Kathmandu district in 1990 (a) and 2010 (b) |
Computer vision algorithms can extract meaningful information from these remote sensing data sources, data such as vegetation cover, water bodies, and urban areas, and classify them into different land-use and land-cover types. This classification can then be used to detect changes over time and monitor the impact of human activities, climate change, and other environmental factors on the land.
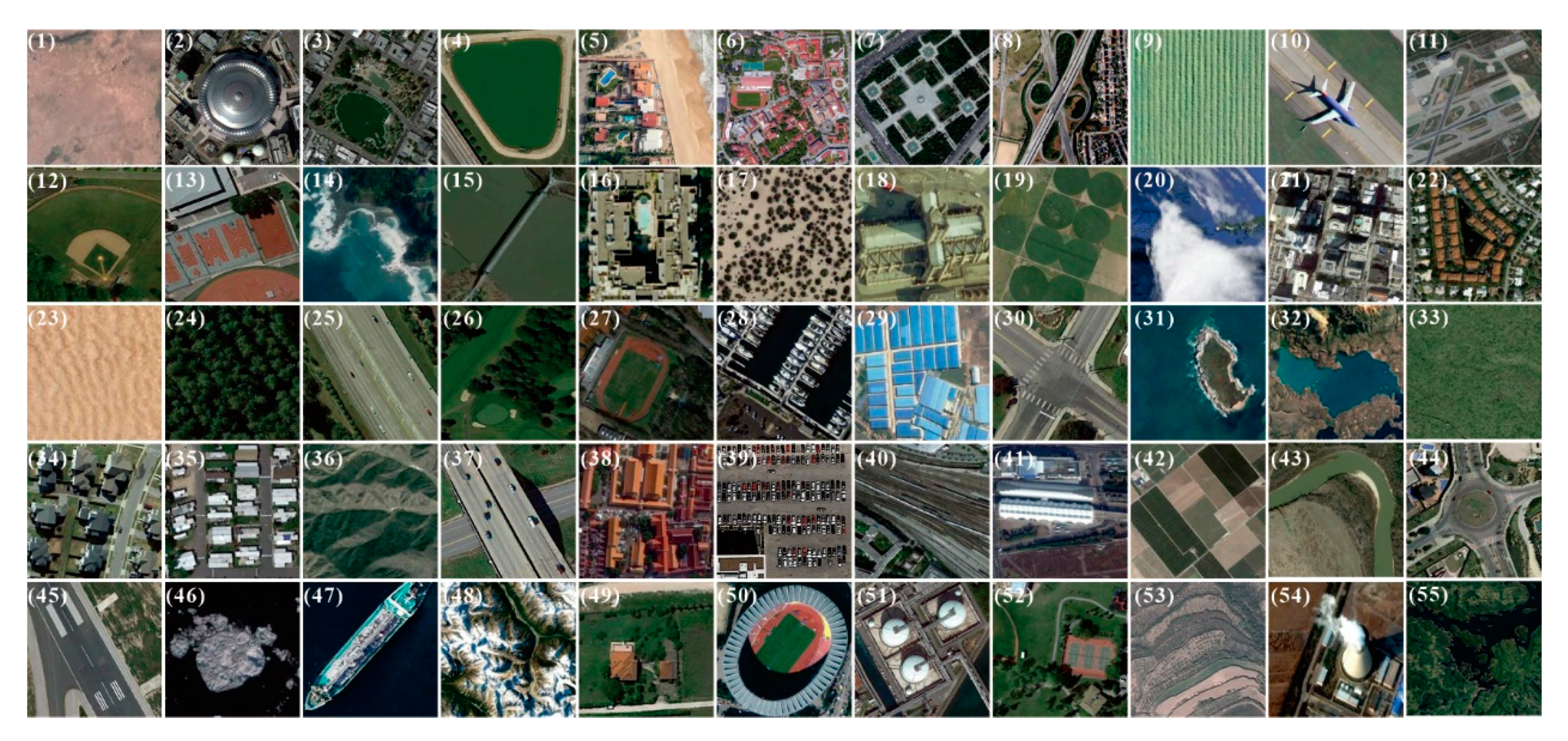 |
|---|
| Samples of satellite imagery showcasing the various scientific fields that remote sensing can offer |
A wide range of remote sensing instruments and methods that can be used for land use/cover change detection, including optical sensors, radar sensors, LiDAR, hyperspectral imaging, supervised classification techniques, deep learning algorithms, and machine learning algorithms. There is also a trend towards using more advanced techniques such as deep learning to improve accuracy and efficiency in detecting land use/cover changes from remote sensing data.
 |
|---|
| Gif of Land-cover change between 2001-2100 under a Business as Usual Scenario in the California Bay Area: a public domain example of a predictive model using remote sensing data |
Overall, computer vision and remote sensing technologies are significant in detecting land-use and land-cover changes around the world as they provide a comprehensive and objective view of the Earth’s surface, enabling better decision-making and management of the environment.